Technology
Platform
BrYet’s technology is based on a proprietary platform that enables the circumvention of sequential cancer-modified biological barriers to maximize efficacy and minimize side effects: Transport Oncophysics.
Transport Oncophysics
A mathematical framework used to:
- Predict where drugs and vaccines will distribute in the body, their efficacy, and adverse side effects;
- Interpret and differentiate cancer phenotypes;
- Personalize treatment in novel ways through transport biomarkers.
This is a unique approach to target desired organs/tissues:
- Nanoporous silicon microparticles manufactured using industry-standard semiconductor materials & processes;
- With precisely controlled physical characteristics to modulate concentration ranges at desired sites;
- And that harmlessly biodegrade into silicic acid and exit through the renal system.
%
Functional Cures
In Pre-Clinical Animal Models
Product
ML-016 (iNPG-pDOX)
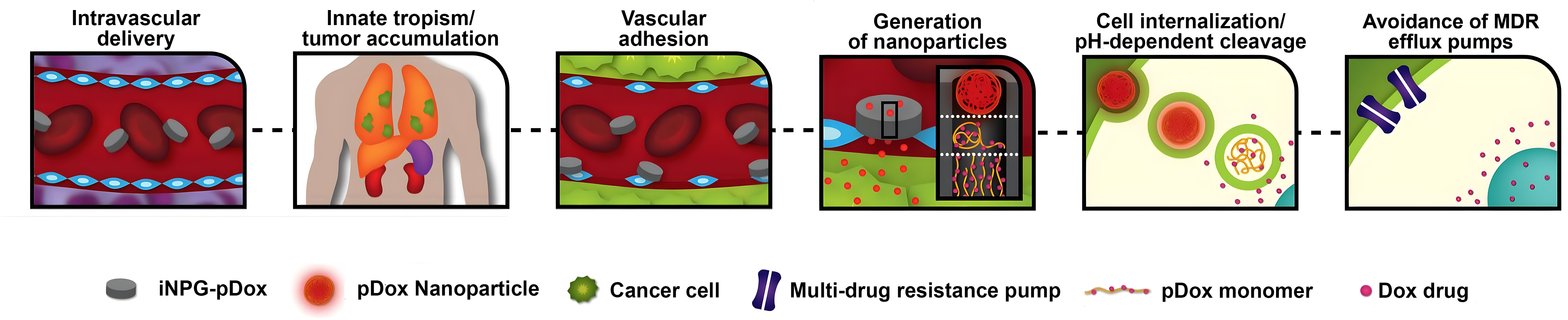
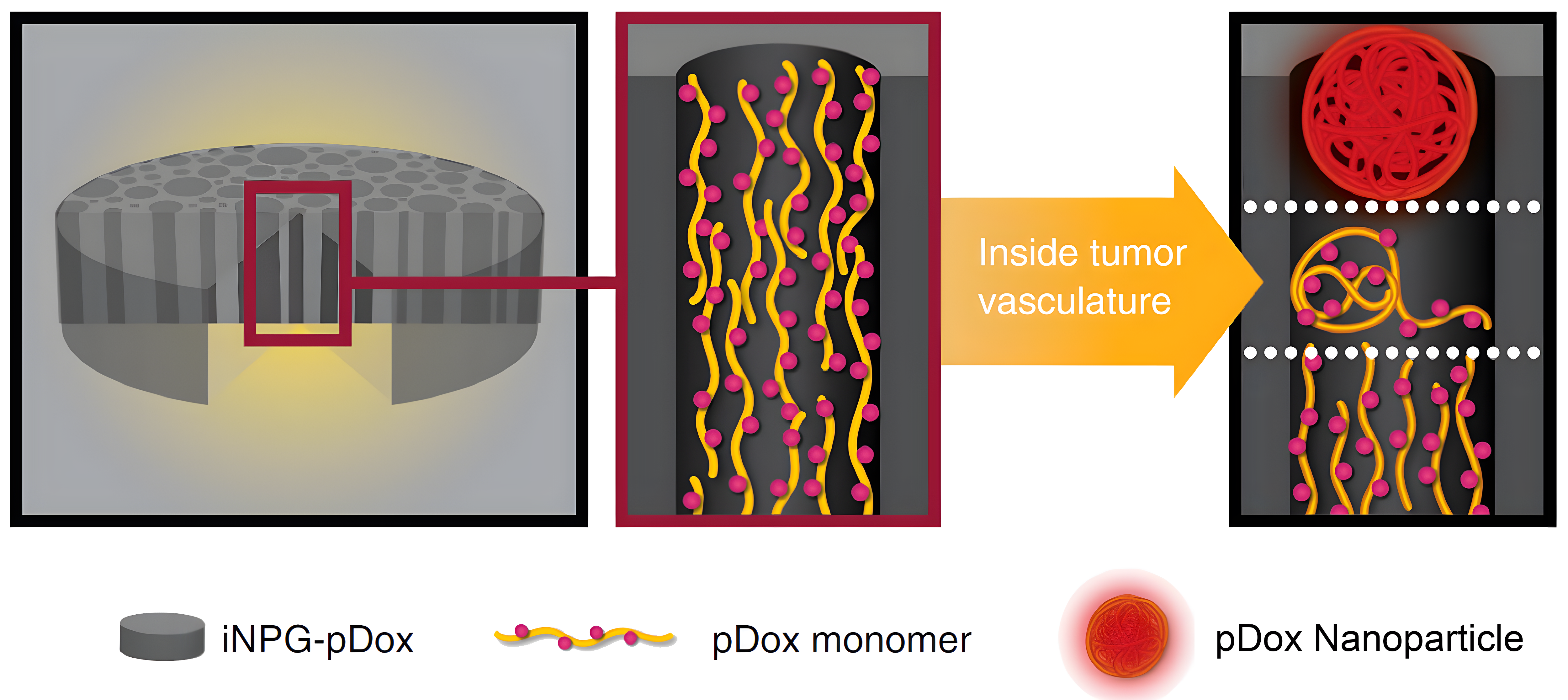
BrYet has identified a lead product from these platforms: ML-016 (iNPG-pDox), a therapeutic agent with unprecedented curative potential for lung and liver metastases, composed of a nanoporous silicon microparticle, linear polymer strands, a chemotherapeutic small molecule and a pH-sensitive linker.
ML-016 (iNPG-pDOX) demonstrated complete functional cures in 40-50% of metastatic mice including treatment resistant cell lines.
Pre-Clinical Results
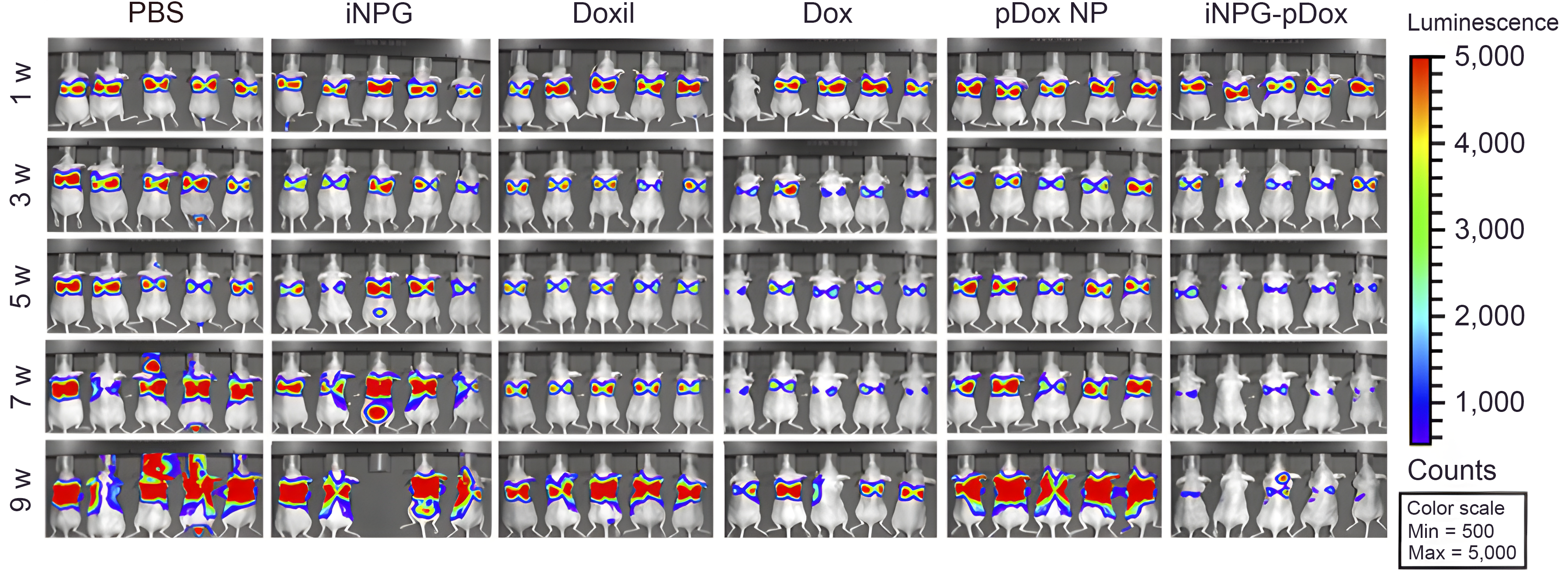
Bioluminescence monitoring of MDA-MB-231 tumor metastasis in the lung was completed. Nude mice were inoculated with MDA-MB-231 cells carrying a luciferase gene, divided into six treatment groups (n = 10 mice/group), and treated weekly with 3 mg/kg free doxorubicin or biweekly with 6 mg/kg Doxil, pDox or iNPG-pDox for 6 weeks. Mice were maintained further thereafter to monitor survival. Images of five mice/group are shown.
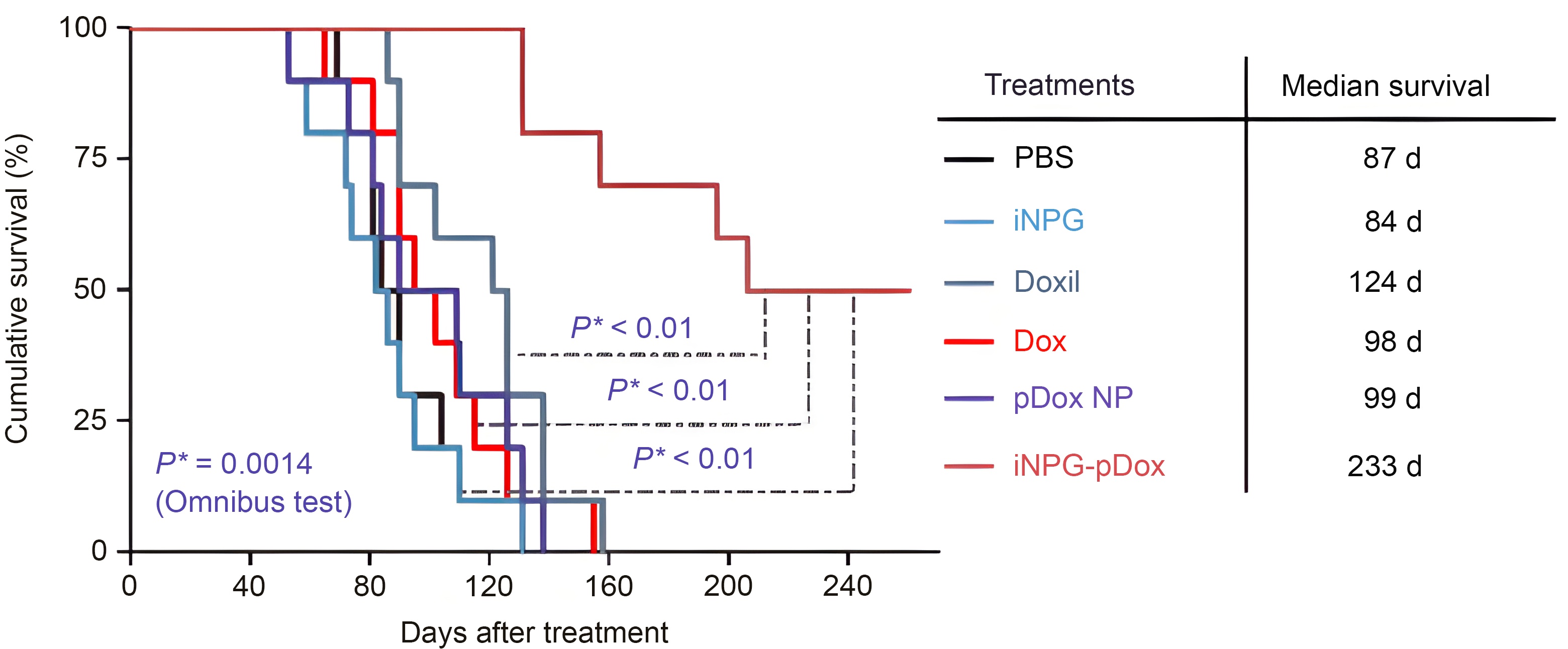
The Kaplan-Meier plot shows animal survival with median survival time listed in the table. Differences in survival were evaluated by the log-rank test. A global test demonstrated a difference exists among the groups. Pairwise comparisons were performed to evaluate the advantage of iNPG-pDox formulation over the clinical formulations.